What is Cloud Cost Optimization?
Cloud cost optimization is the practice of maximizing the efficiency of cloud resource usage to reduce expenses while maintaining the required performance, security, compliance, and availability.
It goes beyond mere cost-cutting, instead focusing on analyzing current cloud usage, identifying inefficiencies, and eliminating waste.
By employing metrics, analytics, and automated tools, you can adapt dynamically to evolving workload requirements and the constantly changing landscape of cloud pricing and services.
Every workload is unique and demands a tailored approach, with performance thresholds defined based on operational data and domain expertise.
Effective cloud cost optimization strategies ensure that resources are allocated appropriately in order to balance operational needs with budget constraints. This enables organizations to achieve the best cloud performance at the lowest possible cost.
Through careful planning and the use of appropriate tools, you can anticipate cost-related challenges, make informed decisions about resource allocation, and maximize the value of their cloud investments.
Top 10 Cloud Cost Optimization Strategies in 2025
1. Stop Guessing: Make Your Cloud Bill Actionable
Your cloud bill isn’t just a receipt, but it’s a map to hidden inefficiencies. But for many teams, it reads like a foreign language. Line items for EC2, EBS, NAT gateways, and inter-region transfers pile up, and by the time Finance flags the overages, it’s too late.
The fix? Translate your cloud bill into engineering terms. Tag workloads by team, environment, or application. Group spend by usage pattern, like long-running services vs. ephemeral jobs. This makes it clear where you're overpaying, underutilizing, or simply guessing.
For example:
- That
m5.4xlargesitting idle in staging? Kill it or right-size it. - That cross-AZ traffic between EKS nodes? Consider rebalancing pods to reduce egress costs.
- That managed database with 1% CPU utilization? You’re paying for high availability you’re not using.
Here are the key components of your cloud bill to understand:
-
Compute Costs: Charges for processing power, influenced by:
- Types and sizes of virtual machines.
- Regional price variations.
- Spot vs. on-demand instances.
- Usage of spot instances.
-
Managed Services Costs: Fees for managed services like databases, calculated based on usage or per-hour rates.
-
Storage Costs: Costs for storing data, affected by:
- Storage type (e.g., object, block).
- Redundancy options.
- Data retrieval and transfer fees.
-
Bandwidth Costs: Charges for data movement (commonly called “egress costs”), including:
- Intra-region and inter-region transfers.
- Data transfers between your cloud and the internet.
-
Support Costs: Fees based on your provider and selected support plan.
-
Discounts and Savings: Reductions from upfront payments, reserved instances, or committed use contracts.
You can’t optimize what you can’t see. And cloud bills don’t speak YAML. But once you break it down into the language of your infra, the savings opportunities become obvious and actionable.
2. Catch Cost Spikes Before They Hurt
Most cloud teams discover cost anomalies in the worst way possible: after they happen. Whether it’s a runaway job, a misconfigured autoscaler, or a forgotten dev environment, small oversights can rack up five-figure bills in days.
By setting benchmarks and configuring notifications, you can act quickly when anomalies occur. Investigating the root cause of anomalies—whether due to legitimate demand changes or issues like misconfigured resources—ensures accurate spending management. Identifying and addressing such issues promptly helps optimize costs and maintain alignment with your planned budget.
3. Use autoscaling to reduce costs
Autoscaling sounds simple: scale up when demand rises, scale down when it drops. But in practice, most teams either overprovision “just in case”, or struggle with underutilized resources they can’t right-size fast enough.
That's where intelligent autoscaling makes a difference and Kubernetes gives you the tools to do it, from HPA and VPA for pods, to Karpenter for node-level autoscaling. But even these can fall short if you’re not optimizing the way your workloads are packed and provisioned.
Tools like CloudPilot AI extend Karpenter’s native capabilities by introducing smarter scheduling strategies, such as automatically picking the optimal instance types, improving bin-packing efficiency, and reducing interruptions from spot instances. This kind of automation helps ensure you’re not just scaling, but doing so with cost in mind.
4. Rightsize Before You Regret It
Rightsizing is one of the fastest ways to reduce cloud waste, yet it's often neglected because it's tedious. Over-provisioned VMs, inflated requests in Kubernetes, and idle services linger because no one has time to track usage patterns across teams or environments.
The key is visibility and automation. You need to:
- Continuously track CPU, memory, and IOPS usage
- Flag underutilized resources
- Adjust instance types, pod requests, or even autoscaler parameters accordingly
Modern tools, including built-in cloud provider recommendations, Kubernetes resource analyzers, and bin-packing-aware schedulers like Karpenter, can help automate much of this.
For teams using CloudPilot AI, rightsizing is integrated into its decision-making engine: instance types and node configurations are selected based not only on fit, but also real-time utilization and cost-performance tradeoffs.
5. Take Advantage of Spot Instances Without the Risk
Spot instances offer huge cost savings, often up to 90% compared to on-demand, but they come with a catch: your instance can be interrupted with as little as 2 minutes' notice. For DevOps and platform teams, this makes spot adoption risky, especially for production workloads.
To use spot instances effectively, you need:
- A clear understanding of which workloads are interruption-tolerant (e.g. batch jobs, CI/CD, large-scale tests)
- A strategy for fault tolerance and failover
- Monitoring tools that help track price volatility and interruption rates
For example, CloudPilot AI includes a Spot Automation feature that uses machine learning to predict interruptions up to 45 minutes in advance across over 7,500 AWS Spot instance types. It can then automatically replace about-to-be-interrupted instances, minimizing disruption with no manual effort.
Want to explore real-time spot pricing, historical trends, and interruption frequencies across instance types? Spot Insights, a free tool from CloudPilot AI, provides that visibility and helps you make smarter decisions before deploying.
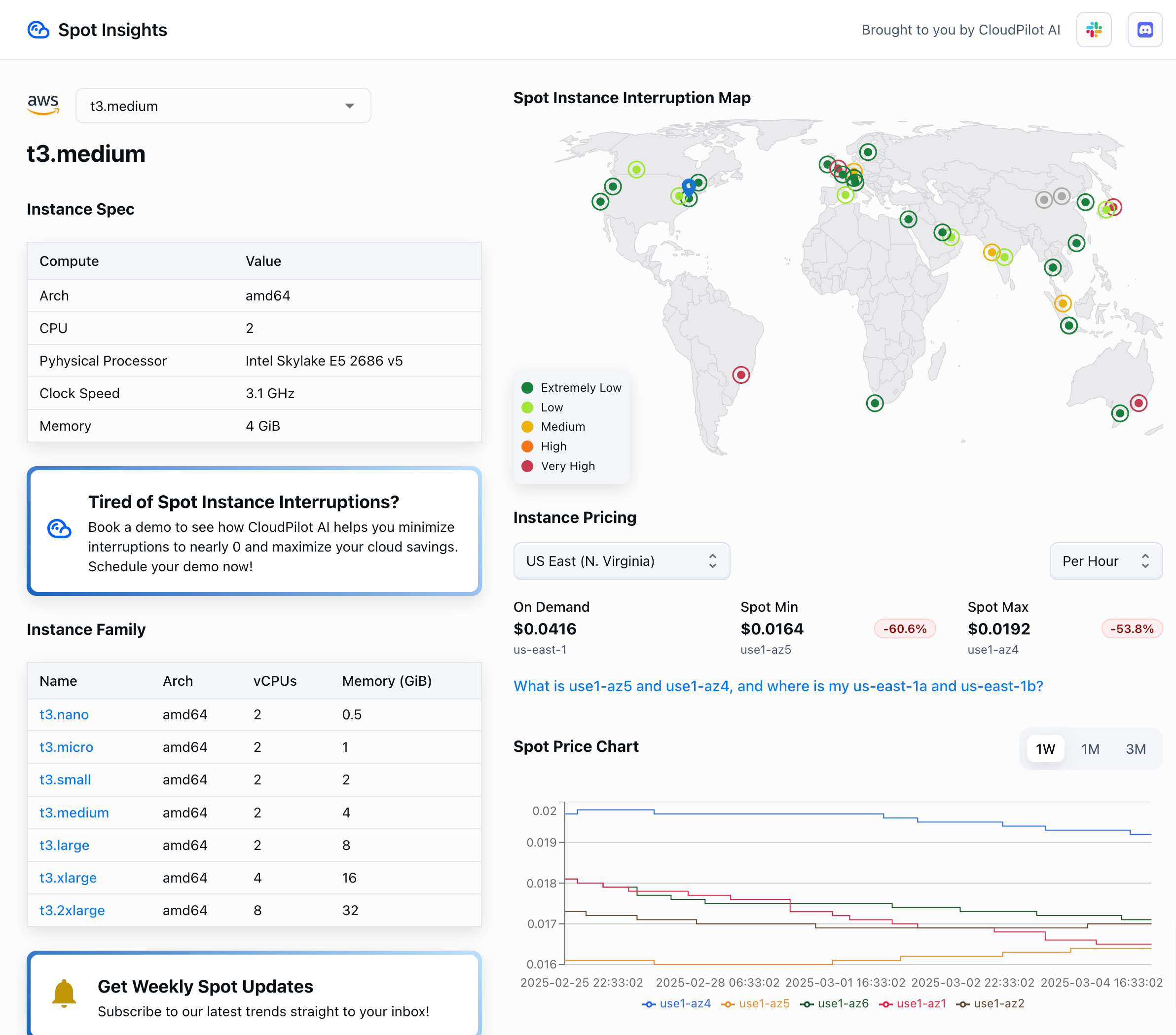
Bottom line: Spot instances are a powerful cost lever, but only if you have the tools and automation to manage their unpredictability.
6. Use Reserved Instances(RI)
Reserved Instances (RIs) are a cost-effective solution for workloads with predictable and consistent resource demands. By committing to a specific capacity for a predetermined period, typically one or three years, you can achieve significant cost savings—up to 75% compared to on-demand pricing. This makes RIs ideal for steady workloads where scaling up or down is unlikely during the commitment period.
To use RIs effectively, follow these strategies:
1. Analyze Usage Patterns: Evaluate historical usage and forecast future demand to identify workloads that consistently require specific resources.
2. Diversify Commitments: Purchase a mix of RIs with different term lengths to balance long-term savings with operational flexibility.
3. Adapt as Needed: Regularly review your RI portfolio to ensure it aligns with evolving workload requirements and make adjustments as necessary.
While RIs require upfront planning and a time commitment, they are an excellent option for reducing costs for stable and predictable workloads. For dynamic or less predictable workloads, consider combining RIs with other options like spot or on-demand instances to optimize overall cloud spending.
7. Identify idle resources
Identifying and eliminating idle resources is a crucial step in optimizing cloud costs. Cloud providers charge for resources even when they’re underutilized or idle, which can quietly inflate your expenses without delivering value. For example, if a server's CPU utilization is only 20%, but you’re paying for 100%, a significant portion of that cost is wasted.
To address this, follow these best practices:
- Regular Monitoring: Use cloud monitoring tools to track key metrics like CPU, memory, disk usage, and bandwidth. Set up alerts to flag resources with consistently low utilization.
- Identify Idle Resources: Look for instances with little to no activity over an extended period, such as databases without significant read/write operations or servers that remain unused.
- Evaluate Necessity: Assess whether these resources are required for future projects or critical operations. If not, consolidate, downsize, or remove them.
There’s no need to retain idle resources for occasional traffic spikes or busy seasons—cloud features like auto-scaling and on-demand options can dynamically allocate resources when needed. By proactively managing idle resources, you can reduce waste and significantly cut cloud costs.
8. Use the correct storage options for your business
Choosing the right storage option is essential for balancing performance and cost in your cloud environment. Cloud providers offer various storage types and tiers, each suited to different data requirements. To make an informed decision, consider the following factors:
1. Access Frequency:
- Use high-performance storage like Amazon EBS or Azure Managed Disks for frequently accessed data requiring low-latency access, such as databases or applications with fast read/write needs.
- For less frequently accessed data, opt for cost-efficient solutions like Amazon S3 Standard-IA or Azure Blob Storage Cool, which reduce costs for data not requiring immediate access.
- For rarely accessed data that must be retained long-term, choose archival storage like Amazon S3 Glacier or Azure Blob Storage Archive. These tiers are ideal for backups or compliance-driven retention.
2. Automation and Flexibility:
- Consider tools like Amazon S3 Intelligent Tiering, which automatically analyzes usage patterns and adjusts data to the most cost-effective tier.
3. Storage Type:
- Evaluate whether object storage, block storage, or file storage best suits your application needs. For instance, backups often fit best in object storage, while high-performance applications benefit from block storage.
By carefully assessing your data's usage patterns, performance needs, and lifecycle requirements, you can choose storage options that minimize costs while meeting your operational demands.
9. Optimize cloud costs at every software development stage
Integrating cost optimization throughout the software development lifecycle (SDLC) ensures efficient cloud usage and minimizes unnecessary spending. By embedding cost-awareness into each phase of development, teams can maximize return on investment (ROI) and maintain budget control. Here's how to implement cost optimization at each stage:
- Planning:
- Assess cloud resource needs based on historical data and projected usage patterns.
- Align budgets with technical requirements to prevent unexpected expenses.
- Design and Development:
- Prioritize cost-efficient architectures and lightweight, scalable application designs.
- Use smaller, less expensive instances for development and testing to reduce costs.
- Testing:
- Leverage automated testing to accelerate processes and minimize resource consumption.
- Use spot instances for non-critical testing environments and remove temporary resources post-testing.
- Deployment:
- Automate deployment to minimize manual errors and reduce resource usage time.
- Use load balancing and auto-scaling to handle varying demands efficiently.
- Monitoring and Maintenance:
- Implement real-time monitoring and set alerts for unusual usage.
- Regularly review and deprecate unused or underutilized resources.
- Updates:
- Test updates on smaller instances before rolling them out to production to reduce potential errors and associated costs.
By making cost optimization a continuous effort, organizations can improve resource efficiency, control operational expenses, and align cloud usage with business objectives throughout the SDLC.
10. Build a Culture Where Cloud Cost Matters
Cloud cost optimization isn’t just a tooling problem — it’s a people problem. Many unnecessary expenses come not from malice, but from everyday decisions: over-provisioned workloads, forgotten dev environments, or lack of visibility into who’s spending what.
To shift from reactive cost-cutting to proactive efficiency, you need to build a culture where cloud cost is part of the conversation, not an afterthought.
1. Make Cost Everyone’s Problem and Everyone’s Opportunity
Engineers should understand the financial impact of their infra decisions. Use real examples (e.g. “this unused staging cluster cost us $2,000 last month”) to show how small actions add up. Short internal workshops or onboarding sessions can go a long way.
2. Share the Numbers, Not Just the Blame
Publish dashboards that show team-level cloud usage. Tools that break down spend by service, namespace, or environment help people spot waste and fix it. Shared visibility creates shared responsibility.
3. Define What “Good” Looks Like
Set clear, realistic standards, like capping idle time on non-prod nodes or tagging every resource by project. These should be lightweight enough not to block velocity, but strong enough to guide behavior.
4. Reward Smart Optimizations
Celebrate teams that eliminate waste or find clever savings (like switching to Spot for CI jobs). Recognition doesn’t have to be monetary, even internal shout-outs or leaderboard-style metrics can motivate behavior change.
Cost awareness isn’t about micromanaging. It’s about giving people the context and tools to make smarter choices — so you save money without slowing down innovation.
Cloud Cost Optimization with CloudPilot AI
Cloud cost optimization isn't just about trimming expenses, it's about running smarter. As cloud environments grow, so does the complexity: overprovisioned workloads, idle resources, and unpredictable spot interruptions quietly drain budgets.
CloudPilot AI helps teams cut through that complexity. Built for Kubernetes, it uses machine learning and intelligent scheduling to reduce cloud costs by up to 80%, without compromising performance or reliability.
From automatically rightsizing workloads, to proactively handling spot interruptions across 7500+ instances, CloudPilot AI ensures your workloads run on the most cost-effective, interruption-aware infrastructure available with no manual tuning.
Start optimizating smarter today—partner with CloudPilot AI to transform your waste into profitability.










